Collection Config Files
In Stoker, you define "collections" for your data. In other systems, these might be referred to as "tables", "objects" or "entities".
Each collection represents a collection in Cloud Firestore, and a page in the Admin UI.
Each collection in stoker has its own file in src/collections.
The following are the options for each collection file.
You can use application state and the Web and Node SDKs in your config files.
General Collection Config
labels
{ collection: string, record: string }
These are the names for the collection. They cannot contains spaces (use underscores), but you can provide a user-friendly set of labels in admin.titles.
collection: The name for the collection, i.e. "Clients".
record: The name for a record in the collection, i.e. "Client".
recordTitleField
string
The field in the collection that will be used as the record's title i.e. "Name".
auth
boolean
Set to true if this collection is a "users" collection.
When set to true, records in the collection can be assigned access credentials.
singleton
boolean
Set to true if the collection will only have one record / page i.e. "Settings"
When set to true, no list page will be shown in the Admin UI. The user will be sent straight to the form page for the single record in the collection.
parentCollection
string
This is an advanced option. Set to the collection's parent collection if this collection will be a subcollection in Firestore. Subcollections are not currently supported in the Admin UI.
softDelete
{ archivedField: string, timestampField: string, retentionPeriod: number }
Enable soft-delete for this collection.
archivedField: Provide the name of a Boolean field. This field will be set to true when the record is soft-deleted.
timestampField: Provide the name of a Timestamp field. This field will be set to the current time when the record is soft-deleted.
retentionPeriod: The number of days after which soft-deleted records will be permananently deleted.
fullTextSearch
string[]
An array of field names. These fields will be searchable.
For collections without preloadCache or serverReadOnly set to true, you will need to set up Algolia. Steps:
- Create an Algolia application for your app.
- Create an index for the collection in your Algolia app, using the exact collection name.
- Set searchable attributes for your index (in the "Configuration" section of the index). These attributes should match the fields provided to
fullTextSearch. - Set facets for your index (in the "Configuration" section of the index). The
tenant_idattribute is required. You will also need to add any fields that your app uses to query records in the collection. This usually means all fields used for filters in the admin app, and all fields used for attribute restrictions. So, if your app filters the collection by "Status", add a "Status" attribute to the facets section.
searchOptions
Record<string, unknown>
Client-side full text search options. Only relevant for roles with the preload cache enabled. Provide MiniSeach settings.
relationLists
{ collection: string, field: string, roles?: string[] }[]
Define "child lists" that will appear in the Admin UI for records in this collection.
For example, a "Clients" collection might have lists of related "Sites", "Quotes" and "Invoices" on its record page.
collection: The collection for the relation list
field: The field in the current collection that relates to the collection above.
roles: The roles that can see this relation list
enableWriteLog
boolean
Set to true to enable the write log for this collection. Every write to a record will be logged in Firestore, creating a history that can be used for data recovery and audit purposes.
indexExemption
boolean
Set to true to exempt this collection from Firestore indexing. Indexes that are reqiuried for your app to function will be re-added automatically. This feature improves performance and reduces costs by minimizing the number of indexes in your database. However, it may prevent you from running queries outside of the standard queries used by your app, for example when performing manual back end data operations.
roleSystemFields
{ field: string, roles?: string[] }[]
By default, the following system fields are not accessible to your app's users:
Created_AtSaved_AtCreated_ByLast_Write_AtLast_Save_AtLast_Write_ByLast_Write_AppLast_Write_Connection_StatusLast_Write_Version
You can make them accessible by defining an array of objects containing the name of a field and the roles that can access that field.
Saved_At and Last_Save_At are safely generated on the server. Created_At and Last_Write_At are set on the client, and may not be reliable. The purpose of these fields is to log when offline writes occured.
allowSchemalessFields
boolean
Set to true to allow fields that are not defined in the schema to be written to records in the collection.
ttl
string
The name of a Timestamp field containing an automatic deletion date for the record i.e. "Expires_At"
Denormalized data is not currently deleted by TTL policies, making it unsuitable for deleting data for privacy purposes.
skipRulesValidation
boolean
Collections with many fields may hit the limit of 1000 expressions per request allowed by Firestore Security Rules. If you see this error you can set this property to true to skip rule validation of writes. Validation will be run post-write in a Cloud Function, and you will get an email if invalid data is submitted.
This option can be set at the field-level if you only want to skip rule validation for a subset of fields.
Alternatively, you can set access.serverWriteOnly to true. This will force all writes to go through the server, validating all fields. The downside of this method is that your app will not be able to perform offline writes.
seedOrder
number
The priority of this collection when seeding test data using stoker seed-data.
queries
{
field: string
range?: boolean
standalone?: boolean
roles?: string[]
}[]
This is an advanced option that is only relevant if you are using Stoker as a headless CMS. This option is handled automatically by the Admin UI.
Define fields that will be indexed for querying.
field: The name of the field.
range: Set to true if the field is a Timestamp field.
standalone: Set to true if the field needs to be indexed independent of sorting.
roles: The user roles that will run the query.
custom.autoCorrectUnique
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Return true to automatically rename duplicate records rather than throwing an error.
Only relevant when access.serverWriteOnly is falsy.
custom.disableOfflineCreate
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Return true to disable adding new records while offline.
custom.disableOfflineUpdate
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Return true to disable updating records while offline.
custom.disableOfflineDelete
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Return true to disable deleting records while offline.
Collection Access Config
Access config is specified using the access property.
serverReadOnly
string[]
An array of roles that must read data via the server. This allows more granular access control (specified in serverAccess at the collection or field level).
This option slows performance and removes offline and realtime capabilites, so it is not recommended unless you absolutely need more granular access control.
serverWriteOnly
boolean
Set to true to force writes through the server.
This option is required if your collection has fields that perform two-way relation writes.
This option is automatically enabled for collections with auth set to true.
The above scenarios aside, we do not recommend enabling this option as it slows performance and removes offline write capablities.
On the other hand, this option can greatly reduce the amount of Firestore Security Rules used by the collection. If you are exceeding the 256KB rules limit, you might consider enabling this option for collections that don't require offline writes.
operations
{
assignable?: boolean | string[]
read?: string[]
create?: string[]
update?: string[]
delete?: string[]
}
Define which roles can perform which CRUD operations for the collection.
Set assignable to true or an array of user roles to allow disabling of access in the user's profile.
auth
string[]
A list of roles that can assign access credentials for this collection.
Only relevant when auth is set to true in the root collection config (above).
Access Control Policies
Stoker allows you to set complex access control policies using simple config.
This config comes in the form of:
- "Attribute restrictions", which restrict a user's access to records with certain attributes.
- "Entity restrictions", where you explicitly define which specific records or groups of records can be accessed by a user. This assignment is done in the user's profile (by an Admin).
attributeRestrictions
Provide an array of the following attribute restrictions:
Record Owner Restriction
Users will only be able to access records that they created themselves.
type RecordOwnerRestriction = {
type: "Record_Owner"
roles: { role: string, assignable?: boolean }[]
operations?: ("Read" | "Create" | "Update" | "Delete")[]
}
roles: The roles that this restriction applies to. If assignable is set to true, this restriction can be removed for individual users.
operations: If provided, the restriction will only apply to the provided operations. The restriction will NOT be applied for unlisted operations.
Record User Restriction
Users will only be able to access records that they have been assigned to.
For example, if the collection has an "Assigned To" field, the user will only be able to access the record if they have been added to that field.
type RecordUserRestriction = {
type: "Record_User"
roles: { role: string, assignable?: boolean }[]
collectionField: string
operations?: ("Read" | "Create" | "Update" | "Delete")[]
}
collectionField: The field that will be used to assign access. Must be a relational field linked to a users collection.
roles: The roles that this restriction applies to. If assignable is set to true, this restriction can be removed for individual users.
operations: If provided, the restriction will only apply to the provided operations. The restriction will NOT be applied for unlisted operations.
Record Property Restriction
Users will only be able to access records that have specified values for a selected field.
For example, if the collection has a "Status" field, you can ensure that a user role only sees "Not Started" and "In Progress" records, but not "Completed" or "Archived" records.
type RecordPropertyRestriction = {
type: "Record_Property"
roles: { role: string, assignable?: boolean, values: string[] }[]
propertyField: string
operations?: ("Read" | "Create" | "Update" | "Delete")[]
}
propertyField: Must be a String field with values set.
roles: The roles that this restriction applies to, and which property values they can access. If assignable is set to true, this restriction can be removed for individual users.
operations: If provided, the restriction will only apply to the provided operations. The restriction will NOT be applied for unlisted operations.
entityRestrictions.restrictions
Provide an array of the following entity restrictions:
Individual Entity Restriction
Assign individual records to a user in their profile.
type IndividualEntityRestriction = {
type: "Individual"
roles: { role: string }[]
singleQuery?: number
}
roles: The roles that this restriction applies to. If assignable is set to true, this restriction can be removed for individual users.
singleQuery: Advanced. Force read operations to get all records in a single API call.
Parent Entity Restriction
Assign all records for a parent record to a user in their profile. For example, you might assign a user "All Sites for Company X" or "All Tasks for Project X".
type ParentEntityRestriction = {
type: "Parent"
roles: { role: string }[]
collectionField: string
singleQuery?: number
}
collectionField: The field that parent records can be selected from. Must be a relational field.
roles: The roles that this restriction applies to. If assignable is set to true, this restriction can be removed for individual users.
singleQuery: Advanced. Force read operations to get all records in a single API call.
Parent Property Entity Restriction
Assign all records for a parent record to a user in their profile, by attribute. For example, you might assign a user "All Sites for Company X in State NY" or "All Tasks for Project X assigned to Team B".
type ParentPropertyEntityRestriction = {
type: "Parent_Property"
roles: { role: string }[]
collectionField: string
propertyField: string
}
collectionField: The field that parent records can be selected from. Must be a relational field.
propertyField: The field that defines the attribute.
roles: The roles that this restriction applies to. If assignable is set to true, this restriction can be removed for individual users.
Soft-deleting assigned records does not block access to them. See softDelete.
entityRestrictions.assignable
string[]
An array of user roles for which entity restrictions can be disabled for individual users.
entityRestrictions.parentFilters
This section lets you apply entity restrictions from a parent collection onto a child collection.
For example, you could assign a user access to "All Jobs on Sites for Company X in State NY" or "All Subtasks on Tasks for Project X assigned to Team B".
Individual Entity Parent Filters
Assign an individual entity restriction from a parent collection.
type IndividualEntityParentFilter = {
type: "Individual"
collectionField: string
roles: { role: string }[]
}
collectionField: The relational field that links to the collection that the individual entity restriction is on.
roles: The roles that this parent filter applies to.
Parent Entity Parent Filters
Assign a parent entity restriction from a parent collection.
type ParentEntityParentFilter = {
type: "Parent"
collectionField: string
parentCollectionField: string
roles: { role: string }[]
}
collectionField: The relational field that links to the collection that the individual entity restriction is on.
parentCollectionField: The relational field that matches the parent entity restriction's collection field.
roles: The roles that this parent filter applies to.
Parent Property Entity Parent Filters
Assign a parent propery entity restriction from a parent collection.
type ParentPropertyEntityParentFilter = {
type: "Parent_Property"
collectionField: string
parentCollectionField: string
parentPropertyField: string
roles: { role: string }[]
}
collectionField: The relational field that links to the collection that the individual entity restriction is on.
parentCollectionField: The relational field that matches the parent entity restriction's collection field.
parentPropertyField: The field that matches the parent entity restriction's property field.
roles: The roles that this parent filter applies to.
When parent filters are used, the collection and property fields used in entity restrictions and parent filters should have updates disabled using restrictUpdate. This is because you will likely be denormalizing data for these fields.
customSecurityRules
boolean
Set to true if you want to write custom Firestore Security Rules for the collection.
Custom security rules can be added at firebase-rules/firestore.custom.rules
You'll probably want to copy the generated security rules for modification before enabling this option.
customStorageRules
boolean
Set to true if you want to write custom Firestore Storage Rules for the collection.
You'll probably want to copy the generated security rules for modification before enabling this option.
permissionWriteRestrictions
permissionWriteRestriction[]
Stoker lets you restrict which permissions a user role can assign to other user roles. For example, imagine a scenario where you want:
- "Manager" users to be able to create any users with any permissions
- "Supervisors" to be able to create "Staff Member" users only. Additionally, Supervisors can only grant access to 3 selected collections and must apply certain attribute and entity restrictions on those collections.
This allows a flexible yet secure hierarchy of access assignment.
Your config should look like this:
type permissionWriteRestriction = {
userRole: string
recordRole: string
collections: {
collection: string
operations: ("Read" | "Create" | "Update" | "Delete")[]
attributeRestrictions?: ("Record_Owner", "Record_User", "Record_Property")[]
restrictEntities?: boolean
auth?: boolean
}[]
}
userRole: The user role you are applying restrictions to.
recordRole: A role that the user above can assign access to.
collections: Define which operations and restrictions are to be applied for each collection.
files
AccessFiles
You can define access rules for file uploads.
Your config should look like this:
type AccessFiles = {
assignment?: {
[role: string]: {
optional?: {
read?: string[]
update?: string[]
delete?: string[]
}
required?: {
read?: string[]
update?: string[]
delete?: string[]
}
}
}
metadata?: {
[key: string]: string
}
customMetadata?: {
[key: string]: string
}
}
assignment: Define the user roles that the user must assign access to for each file.
metadata: Enforce Firebase Storage metadata constraints.
customMetadata: Enforce custom metadata constraints.
For example:
{
assignment: {
Client: {
required: {
read: ["Manager, "Supervisor"]
update: ["Manager, "Supervisor"]
delete: ["Manager]
}
}
},
metadata: {
size: " <= (5 * 1024 * 1024)",
contentType: ' in ["application/octet-stream"]',
},
customMetadata: {
collection: ' == "Work_Orders"',
},
}
custom.serverAccess
{
read?: (role: string, record?: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
create?: (role: string, record: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
update?: (role: string, record: StokerRecord, originalRecord?: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
delete?: (role: string, record: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
}
Define additional access control using code on the server.
Only relevant if access.serverWriteOnly is set to true.
Return a boolean indicating whether or not the access check passed.
This code is not sent to the client.
Preload Cache Config
You can preload data for your collections on app startup. Preloaded data is cached and is available for the lifetime of the session.
Since Stoker is primarily designed for enterprise applications, long sessions are common. It is also common for users to download the app onto the desktop as a PWA.
Because long sessions are common, we encourage preloading data on app startup. This results in a snappy application that works offline thanks to cached data.
We absolutely recommend using the preload cache for time series data. This will result in huge performance gains, more available features and fewer indexes used. You don't have to preload huge amounts of data if you don't want to.
To enable preloading of data, use the preloadCache property.
For examples of this config, see the default Inbox and Outbox collections in your project (created by stoker init).
roles
string[]
An array of user roles that will use the preload cache.
relationCollections
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Whether to wait for related collections to load before signalling to the app that the collection is loaded.
range
PreloadCacheRange
Use this option to preload a range of time-series data. The user will be able to update the preloaded range using a date picker in the Admin UI.
type PreloadCacheRange = {
fields: string[]
ranges?: [string, string][]
labels?: string[]
start: "Today" | "Week" | "Month" | "Year" | Date | number
startOffsetDays?: number
startOffsetHours?: number
end?: Date | number
endOffsetDays?: number
endOffsetHours?: number
selector?: "range" | "week" | "month" | ("range" | "week" | "month")[]
}
fields: An array of Timestamp fields in the collection that time-series data can be preloaded by. The user will be able to select which field to preload data by.
ranges: An array of ranges of data that can be preloaded. For example ["Start", "End"]. This will preload all data that overlaps with the range selected by the user. Fields used must also be defined in fields above.
labels: Human-readable labels for the fields listed above, if they are not already human-readable, i.e. the field names contain underscores.
start: The default start date for the preloaded range.
startOffsetDays: Offset the default start date by x days
startOffsetHours: Offset the default start date by x hours
end: The default end date for the preloaded range.
endOffsetDays: Offset the default end date by x days
endOffsetHours: Offset the default end date by x hours
selector: Whether the range picker should show the week, month or custom range selectors.
constraints
[string, WhereFilterOp, unknown][] | (() => [string, WhereFilterOp, unknown][] | Promise<[string, WhereFilterOp, unknown][]>)
Additonal Firestore constraints to apply to the preload cache. This is an advanced option.
Collection Fields Config
Fields are specified using the fields property.
fields must be an array of field objects. These objects are outlined below.
General Field Properties
These properties can be set on any field type.
name
string
The name of the field. It must not have spaces (use underscores). You can set a human-readable name in admin.label.
access
string[]
An array of user roles that can access the field.
Omitting the access property altogether allows access by ALL roles.
restrictCreate
boolean | string[]
Set to true to prevent this field from being included when the record is created.
Alternatively, provide an array of user roles that CAN provide the field when creating a record.
restrictUpdate
boolean | string[]
Set to true to prevent this field from being changed when the record is updated.
Alternatively, provide an array of user roles that CAN change the field when updating a record.
required
boolean
Set to true if the field is a required field.
nullable
boolean
Set to true if the field is a nullable field.
sorting
boolean | { direction?: "asc" | "desc" roles?: string[] }
Specifies that this field will be used for sorting. Not required if all user roles have preloadCache or access.serverReadOnly enabled. In these cases, sorting is automatic.
Set to true to sort by "asc" and "desc" for all user roles, or provide the more granular config above.
Specifying a sorting direction for a field in a collection without preloadCache or serverReadOnly set to true will result in the "Previous" page button being disabled. The "Back to start" button will still work.
skipRulesValidation
Skip Firestore Security Rules validation for this field. This can help to keep the size of the security ruleset down. When this option is enabled, validation will be performed post-write in a Cloud Function. You will receive an email if invalid data has been submitted.
description
string | (() => string | Promise<string>)
A description for the field for LLMs. Only relevant if ai is configured.
singleFieldExemption
{
queryScope: "COLLECTION" | "COLLECTION_GROUP"
order?: "ASCENDING" | "DESCENDING"
arrayConfig?: "CONTAINS" | "CONTAINS_ANY"
}
Place a single field exemption on the field in Firestore.
If you have set indexExemption at the collection level, this option will re-enable indexing for the field.
You should consider exempting incrementally increasing monotonic fields, large String fields, Map fields and Array fields.
custom.initialValue
unknown | ((record?: StokerRecord) => unknown | Promise<unknown>)
Calculate an initial value for this field when creating the record.
custom.serverAccess
{
read?: (role: string, record?: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
create?: (role: string, record: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
update?: (role: string, record: StokerRecord, originalRecord?: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>
}
Define additional access control using code on the server.
Only relevant if access.serverWriteOnly is set to true.
Return a boolean indicating whether or not the access check passed.
This code is not sent to the client.
String Field Properties
type
"String"
values
string[]
An optional list of values. This will result in a dropdown list being shown in the Admin UI.
unique
Set to true to make the field a unique field. Be sparing with this option unless access.serverWriteOnly is set to true.
Case is ignored when determining whether or not a value is a duplicate.
You can auto-rename duplicate values in the Web SDK using custom.autoCorrectUnique. Note that this will append an identifier i.e. "DUPLICATE-1" to the end of the field value. Your field validation strategy will need to account for this identifier, or writes will be rejected.
Unique field values are NOT freed up when a record is soft-deleted.
length
number
Specify a fixed length for the field.
minlength
number
Specify a minimum length for the field.
maxlength
number
Specify a maximum length for the field.
pattern
string
Specify a regex pattern for the field.
email
boolean
Set to true if the field is an email address
Emails are currently only validated server-side if you have access.serverWriteOnly set to true. You can alternatively use pattern above, which is always validated server-side.
url
boolean
Set to true if the field is a url
URLs are currently only validated server-side if you have access.serverWriteOnly set to true. You can alternatively use pattern above, which is always validated server-side.
emoji
boolean
Set to true if the field is an emoji
Emojis are currently only validated server-side if you have access.serverWriteOnly set to true. You can alternatively use pattern above, which is always validated server-side.
uuid
boolean
Set to true if the field is a UUID
UUIDs are currently only validated server-side if you have access.serverWriteOnly set to true. You can alternatively use pattern above, which is always validated server-side.
ip
boolean
Set to true if the field is an IP address
IP addresses are currently only validated server-side if you have access.serverWriteOnly set to true. You can alternatively use pattern above, which is always validated server-side.
Number Field Properties
type
"Number"
values
number[]
An optional list of values. This will result in a dropdown list being shown in the Admin UI.
unique
Set to true to make the field a unique field. Be sparing with this option unless access.serverWriteOnly is set to true.
Unique field values are NOT freed up when a record is soft-deleted.
autoIncrement
boolean
Set to true to make the field an auto-incremented number.
Auto-incremented numbers are written by a Cloud Function after the record has been saved to the server. This means auto-incremented numbers made in offline mode won't appear until the user has reconnected.
decimal
number
Set the maximum number of decimal places for this field.
min
number
Set the minimum number value for this field.
max
number
Set the maximum number value for this field.
Timestamp Field Properties
type
"Timestamp"
values
number[]
An optional list of dates in milliseconds format. This will result in a dropdown list being shown in the Admin UI.
min
number
Set the minimum milliseconds value for this field.
max
number
Set the maximum milliseconds value for this field.
Array Field Properties
type
"Array"
values
string[]
A list of values. A dropdown selector will be shown in the Admin UI.
length
number
Set the exact required length for this field.
minlength
number
Set the minimum length for this field.
maxlength
number
Set the maximum length for this field.
Map Field Properties
type
"Map"
Relational Field Properties
Stoker records are limited to Firestore's per-document limits:
- 1MB max document size
- 40,000 max index enrtries
This limits the maximum number of relations you can have per document.
type
"OneToOne" | "OneToMany" | "ManyToOne" | "ManyToMany"
collection
string
The collection for the relational field.
includeFields
string[]
Save fields from the related record to the target record. Field values will be denormalized and will automatically update when the source record is updated.
This architecture avoids the N+1 problem and gives you a snappy, offline-friendly app. The downside is that potentially large back-end write operations are required when values change. However, these write operations are automatically managed by highly scalable Cloud Functions in Stoker.
For examples of this config, see the "Sender" and "Recipients" fields in the default Inbox collection in your project (created by stoker init)
Updates to include fields are written by a Cloud Function after the source record has been updated on the server. This means include field updates made in offline mode won't appear until the user has reconnected.
titleField
string
Choose one of the includeFields values above to act as the title field for the related record.
For examples of this config, see the "Sender" and "Recipients" fields in the default Inbox collection in your project (created by stoker init)
dependencyFields
{ field: string, roles: StokerRole[] }[]
Grant users access to the specified field in the related collection. For example, you could assign a user access to only the "ID" and "Name" fields in the related collection. This lets users select values from a dropdown without giving them full access to the related collection.
For an example of this config, see the "Recipient" field in the default Outbox collection in your project (created by stoker init)
Only records allowed by the user role's access policy for the related collection will be accessible.
twoWay
string
Enable a two-way relation.
Provide the name of a relational field in the target collection to link with. The following link types are valid:
OneToOne > OneToOne
OneToMany > ManyToOne
ManyToOne > OneToMany
ManyToMany > ManyToMany
access.serverWriteOnly must be enabled for this feature to work, which will result in the loss of offline write capabilities.
For two-way writes to work, the user must have write access to both the source record and the target record. Ensure that the user will have:
- Sufficient access to the target record's collection
- Sufficient access to the target record (ensure that Access control policies won't block access to the target record)
- Sufficient access to the target field (
field.access)
preserve
boolean
Set to true to preserve relation data when the related record is deleted.
This may have privacy implications
writeAny
boolean
Set to true to allow users to write any value to the relational field. By default, users can only write values for records that they have access to.
This may have security implications
constraints
[string, "==" | "in", unknown][]
Set Firestore where() query constraints that will be applied when retrieving records for the dropdown selector.
enforceHierarchy
{ field: string, recordLinkField: string }
Enforce the relational integrity of the field. For example, ensure that the record's "Site" is actually related to the record's "Company".
field: Another relational field in the collection that is above the current field in the relational hierarchy.
recordLinkField: The field in the field above's collection that has the same collection as the current field.
length
number
Set the exact number of relations required for this field.
min
number
Set the minimum number of relations for this field.
max
number
Set the maximum number of relations for this field.
When a record is deleted from Stoker, its relation values in other records are deleted. This happens in a Cloud Function, so deletions made in offline mode won't be visible until the user has reconnected.
Computed Field Properties
type
"Computed"
formula
(record: StokerRecord, retrieverData?: any) => string | number | Promise<string | number>
Calculates the value for the field.
When using getSome or subscribeMany, retrieverData will return the data provided by the collection's retriever function. This lets you load data sets for your computed field formulas once per query.
Field Admin UI Properties
Admin UI config is specified using the admin property.
label
string | (() => string)
A human-readable name for the field. Only necessary if name is not human-readable.
listLabel
string | (() => string)
Override the field name shown in the list view.
icon
{ component: React.FC, className?: string } | (() => { component: React.FC, className?: string } | Promise<{ component: React.FC, className?: string } >)
An icon that will be shown for the field on the form page. Provide additional Tailwind classess using className.
condition
{
list?: boolean | ((parentCollection?: CollectionSchema, parentRecord?: StokerRecord) => boolean)
form?: boolean | ((operation?: "create" | "update", record?: StokerRecord) => boolean)
}
Show or hide the field in the list view and on the form page.
The list function recieves the parent collection and parent record when shown on a relation list page.
hidden
"sm" | "md" | "lg" | "xl" | "2xl" | ((record?: StokerRecord) => "sm" | "md" | "lg" | "xl" | "2xl")
The screen size at which the field should be hidden from the list view. This is useful for responsiveness.
readOnly
boolean | ((operation?: "create" | "update", record?: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Return true to set this as a read-only field in the Admin UI
sort
(record?: StokerRecord) => unknown
The returned value will be used for sorting in the list view.
column
boolean | number | (() => boolean | number)
Set the position of the field in the list and the form. Defaults to the position of the field in the fields array, so this option may not be necessary.
description
{
message: string | ((record?: StokerRecord) => string | Promise<string>)
condition?: boolean | ((record?: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
}
Display a conditoinal description message under the field in the Admin UI.
live
boolean
Set to true to have the field live-update on the form page when the record is updated remotely.
switch
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Set to true on a Boolean field to make it a switch
textarea
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Set to true on a String field to make it a textarea
richText
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Set to true on a Map field to make it a rich text field
italic
boolean | ((record?: StokerRecord) => boolean)
Set to true on a String field to make it italic
currency
string | ((record?: StokerRecord) => string)
Set to a currency symbol on a String field to make it a currency
radio
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Set to true on a String field with values to make it a radio group
slider
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Set to true on a Number field to make it a slider
time
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Set to true on a String field to make it a time field.
Set to true on a Timestamp field to make it a datetime field.
location
{ center: { lat: number, lng: number }, zoom: number }
Set on an Array field to make it a coordinates field.
Provide starting location coordinates and zoom.
image
boolean | (() => boolean)
Set on a String field to make it an image field. Images can be uploaded, or selected from files uploaded to the record.
badge
boolean | string | ((record?: StokerRecord) => boolean | string)
Set on a String field to make it a badge. Return a Tailwind class specifying the color for the badge.
tags
string[] | (() => string[])
For Array fields. Provide an array of Tailwind classes to have values appear as colored badges. The order of the Tailwind classes array must be the same as the field's values array.
noExport
boolean | (() => boolean)
Set to true to exclude this field from CSV export
exportSeparator
string | (() => string)
Set on an Array or relational field to specify the separator to be used between items in CSV export. Defaults to ", ".
modifyDisplayValue
(record?: StokerRecord, context?: "card" | "form" | "list") => unknown
Modify the displayed value for the field, for example when shown in the list view or when read-only on a form.
skipFormRequiredValidation
boolean | (() => boolean)
Set to true to skip required validation on the form page. This is useful if the required field value will be set after the form has been submitted, for example in custom.initialValue or a hook.
overrideFormRequiredValidation
(operation: "create" | "update", record?: StokerRecord) => boolean
Conditionally set a field to "required". This overrides required above, however required above will still be enforced on the server if present.
filterValues
(value: string | number, parentCollection: CollectionSchema, parentRecord?: StokerRecord) => boolean
Filter the options in the dropdown for String or Number fields with values set.
filterResults
(result: SearchResult, parentCollection: CollectionSchema, parentRecord?: StokerRecord) => boolean
Filter the options in the dropdown for relational fields. Only works when preloadCache is enabled for the user's role.
modifyResultTitle
(
record: StokerRecord,
parentCollection: CollectionSchema,
parentRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => string
Modify the results in the dropdown for relational fields.
customListView
(
record?: StokerRecord,
parentCollection?: CollectionSchema,
parentRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => {
component: React.FC
props?: Record<string, unknown>
receiveClick?: boolean
}
Return a custom component to be used in the list view. Set receiveClick to true to have the component receive the click and override the default behaviour of navigating to the record page.
Field Hooks
Fields can have any of the hooks defined in Collection Hooks. Add them to the field's custom property.
Server code protection: During the build process, server-only code blocks are automatically stripped from the client bundle:
if(sdk === "node")blocks are removedelseandelse ifblocks followingif (sdk === "web")guards are removed- Code in
src/nodeis stripped to export names only
Important: Code outside of these guard blocks WILL be sent to the client and will run on the client.
For highly sensitive server operations, consider using custom cloud functions instead.
AI Chat Config
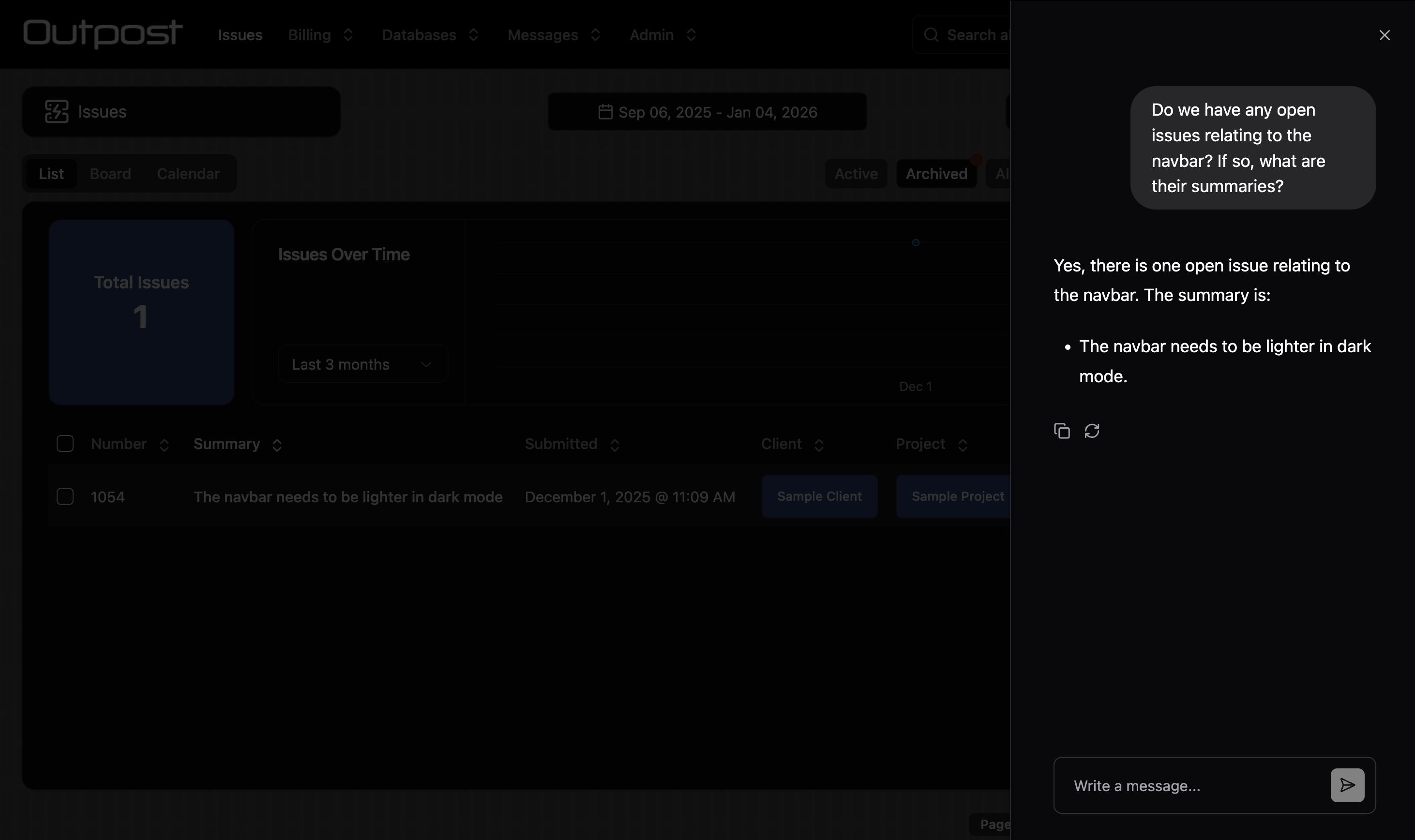
{
embedding?: boolean
chat?: {
name: string
defaultQueryLimit?: number
roles: string[]
}
}
You can enable an AI chat bot for the collection. The chat bot uses Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) to converse with the user about the data in the collection.
embedding: Set to true to save embeddings for records in this collection. This will only work if the custom.setEmbedding hook has been enabled.
chat.name: The name for the chat bot. This is not currently used anywhere, but may be in future.
chat.defaultQueryLimit: The number of documents the LLM should retrieve for context.
chat.roles: The roles that can view the chat bot.
Only assign AI chat access to roles that have access to ALL fields used to calculate embeddings!
Admin UI Config
Admin UI config is specified using the admin property.
hidden
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Return true to hide the collection in the Admin UI.
navbarPosition
number | (() => number)
The collection's position in the navbar.
titles
{ collection: string, record: string } | (() => { collection: string; record: string } | Promise<{ collection: string; record: string }>)
Human-readable labels for the collection. Only necessary if the root labels are not human-readable.
icon
React.FC | (() => React.FC | Promise<React.FC>)
An icon component for the collection. We recommend using Lucide icons, which are bundled with Stoker.
itemsPerPage
number | (() => number | Promise<number>)
The number of items to show per page.
statusField
{ field: string, active?: unknown[], archived?: unknown[] }
Define a field that will be used to sort records into "Active" and "Archived" lists.
For example: { field: "Status", active: ["Not Started", "In Progress"], archived: ["Completed"]}
breadcrumbs
string[] | (() => string[] | Promise<string[]>)
Return an array of relational field names that will be used to show breadcrumbs at the top of the record page.
duplicate
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Return true to show the Duplicate button on the form page.
convert
type Convert = {
collection: string
convert: (record: StokerRecord) => Partial<StokerRecord> | Promise<Partial<StokerRecord>>
roles?: string[]
}
Convert[] | (() => Convert[] | Promise<Convert[]>)
Converting a record creates a new record in the target collection and keeps the original.
Return an array of objects defining which collections records can be converted to. A "Convert" button will be shown on the form page.
collection: The collection to convert records to.
convert: A function that modifies the record before conversion.
roles: The roles that can perform this conversion.
defaultRoute
string | (() => string)
The default route for the record page. Can be "edit", "files", a relation list collection name or a custom form page url.
defaultSort
{ field: string, direction?: "asc" | "desc" } |
(
() => { field: string, direction?: "asc" | "desc" } |
Promise<{ field: string, direction?: "asc" | "desc" }>
)
The default field to sort the list by.
rangeSelectorValues
"range" | "week" | "month" | ("range" | "week" | "month")[] | (() => "range" | "week" | "month" | ("range" | "week" | "month")[])
The date range selector options to be shown to the user.
Only relevant when preloadCache.range is present.
defaultRangeSelector
"range" | "week" | "month" | (() => "range" | "week" | "month")
The default date range selector to be shown to the user.
Only relevant when preloadCache.range is present or a range filter has been applied.
disableRangeSelector
boolean | (() => boolean)
Disable the date range selector for the user.
restrictExport
string[] | (() => string[] | Promise<string[]>)
Restrict CSV export to the defined roles.
addRecordButtonOverride
(record?: StokerRecord) => void | Promise<void>
Provide a function that will override the default behaviour of opening the add record form.
hideCreate
boolean | ((relationList?: string) => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Hide the add record button.
disableUpdate
boolean | ((operation: "create" | "update", record: StokerRecord) => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Disable the edit record form.
This option only disables editing client side. Do not use it if you need to securely block record updates. Use restrictUpdate or operations instead.
onFormOpen
(operation: "create" | "update", record: StokerRecord) => void | Promise<void>
A hook that fires when the record form is opened.
onChange
(
operation: "create" | "update",
record: StokerRecord,
originalRecord: StokerRecord,
) => Partial<StokerRecord> | void | Promise<Partial<StokerRecord> | void>
A hook that fires whenenver the form is updated. Optionally return an object with field updates.
live
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Set to true to have the form page live-update when the record is updated remotely. This can also be configured at the field-level.
Live forms reduce the risk of conflicts and are great for collaboration. However, on a live form remote updates will overwrite local changes. This introduces a risk of data loss. Choose wisely!
meta
{ title?: string, description?: string } | (() => { title?: string, description?: string } | Promise<{ title?: string, description?: string }>)
Define a custom meta title and description for the collection's pages.
rowHighlight
type RowHighlight = {
condition: (record: StokerRecord) => boolean
className: string
roles?: string[]
}
RowHighlight[] | (() => RowHighlight[])
Highlight rows in the list view.
condition: Return true to highlight the row for the given record.
className: The Tailwind classes to be applied to the highlighted row.
roles: The user roles to highlight rows for.
formButtons
type FormButton = {
title: string
icon?: React.FC<{ className?: string }>
variant?: "default" | "destructive" | "outline" | "secondary" | "ghost" | "link"
action: (
operation: "create" | "update" | "update-many",
formValues: StokerRecord,
originalRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => void | Promise<void>
condition?: boolean | ((operation: "create" | "update" | "update-many", record?: StokerRecord) => boolean)
setIsLoading?: (isLoading: boolean) => void
}
FormButton[] | (() => FormButton[] | Promise<FormButton[]>)
Show custom buttons at the bottom of the edit record form.
title: The title text for the custom button
icon: The icon shown on the button
variant: The style of the button
action: The function that fires when the button is clicked
condition: Show or hide the button
setIsLoading: A loading function that will be called when the button is pressed.
formUpload
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Show a file upload button on the add record form.
formImages
boolean | (() => boolean | Promise<boolean>)
Show an image carousel at the top of the edit record form. All image files uploaded to the record will be displayed.
formLists
type FormList {
collection: string
fields: string[]
sortField?: string
sortDirection?: "asc" | "desc"
label?: string
}
FormList[] | (() => FormList[] | Promise<FormList[]>)
Show relation lists directly on the edit record form page.
collection: The collection to show the relation list for
fields: Which columns to show in the list
sortField: The field to sort records by
sortDirection: The direction to sort records by
label: The title for the relation list
customFields
type CustomField = {
position?: number | ((record?: StokerRecord) => number)
component?: React.FC
props?: Record<string, unknown>
condition?: (operation: "create" | "update" | "update-many", record?: StokerRecord) => boolean
}
CustomField[] | (() => CustomField[] | Promise<CustomField[]>)
Create custom form field components.
position: The position of the custom component in the form
component: The React component
props: Props to be passed to the React component
condition: Show or hide the custom component
customRecordPages
type CustomRecordPage = {
title: string
icon?: React.FC<{ className?: string }>
url: string
component: React.FC<{
record: StokerRecord | undefined
collection: CollectionSchema
components: any
hooks: any
utils: any
}>
condition?: (record: StokerRecord | undefined) => boolean
}
CustomRecordPage[] | (() => CustomRecordPage[] | Promise<CustomRecordPage[]>)
Create custom pages for the collection.
title: The title for the custom page in the sidebar
icon: The icon to be shown in the sidebar
url: The url that the page will load on
component: The custom component and the props that will be passed to it.
condition: Show or hide the custom component
retriever
() => any | Promise<any>
Use this method to load data for use in your computed fields.
list
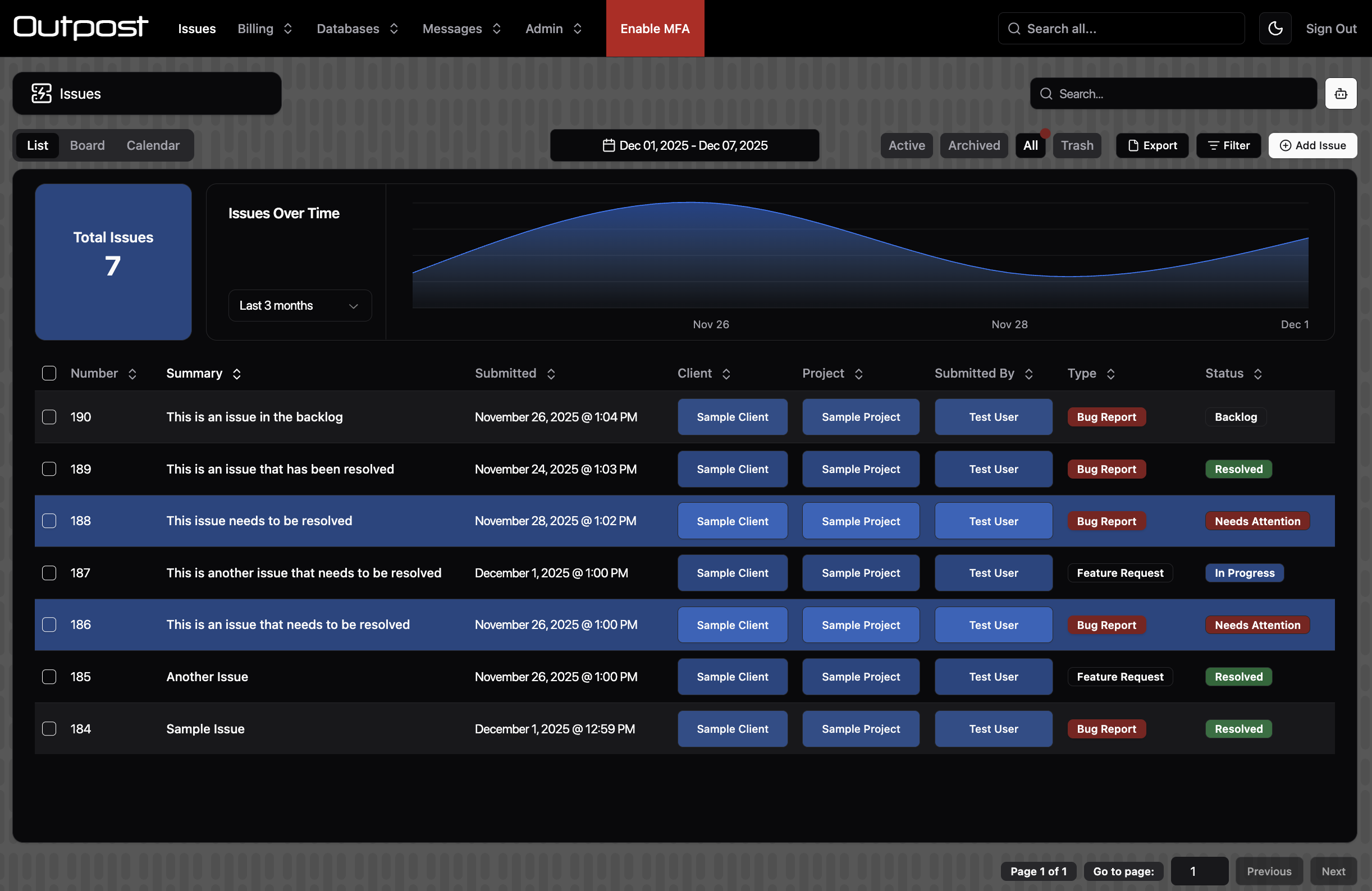
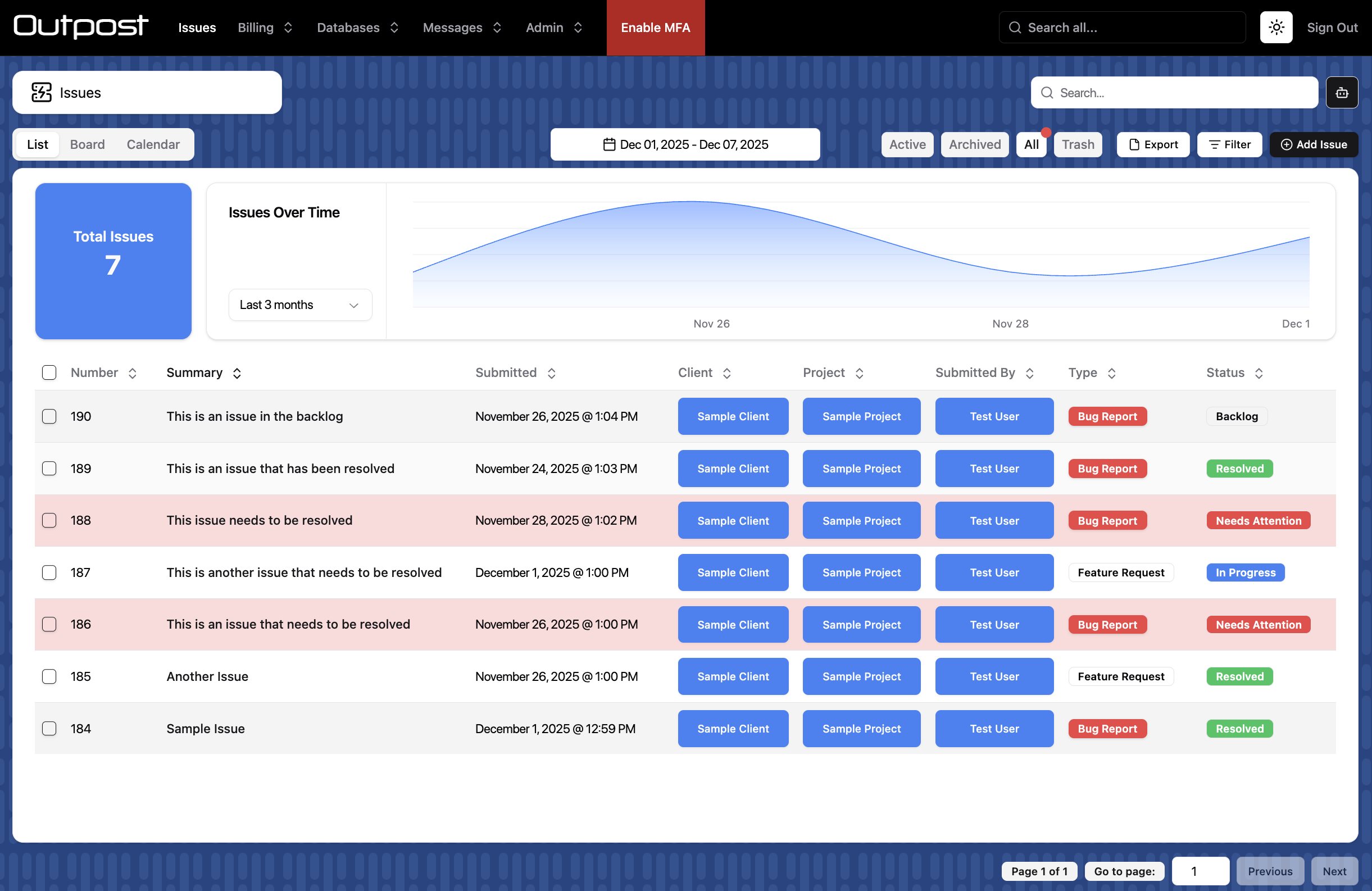
{ title?: string } | (() => { title?: string } | Promise<{ title?: string }>)
Customise the title for list tab. Defaults to "List".
cards
Show a board view with drag and drop and infinite scroll.
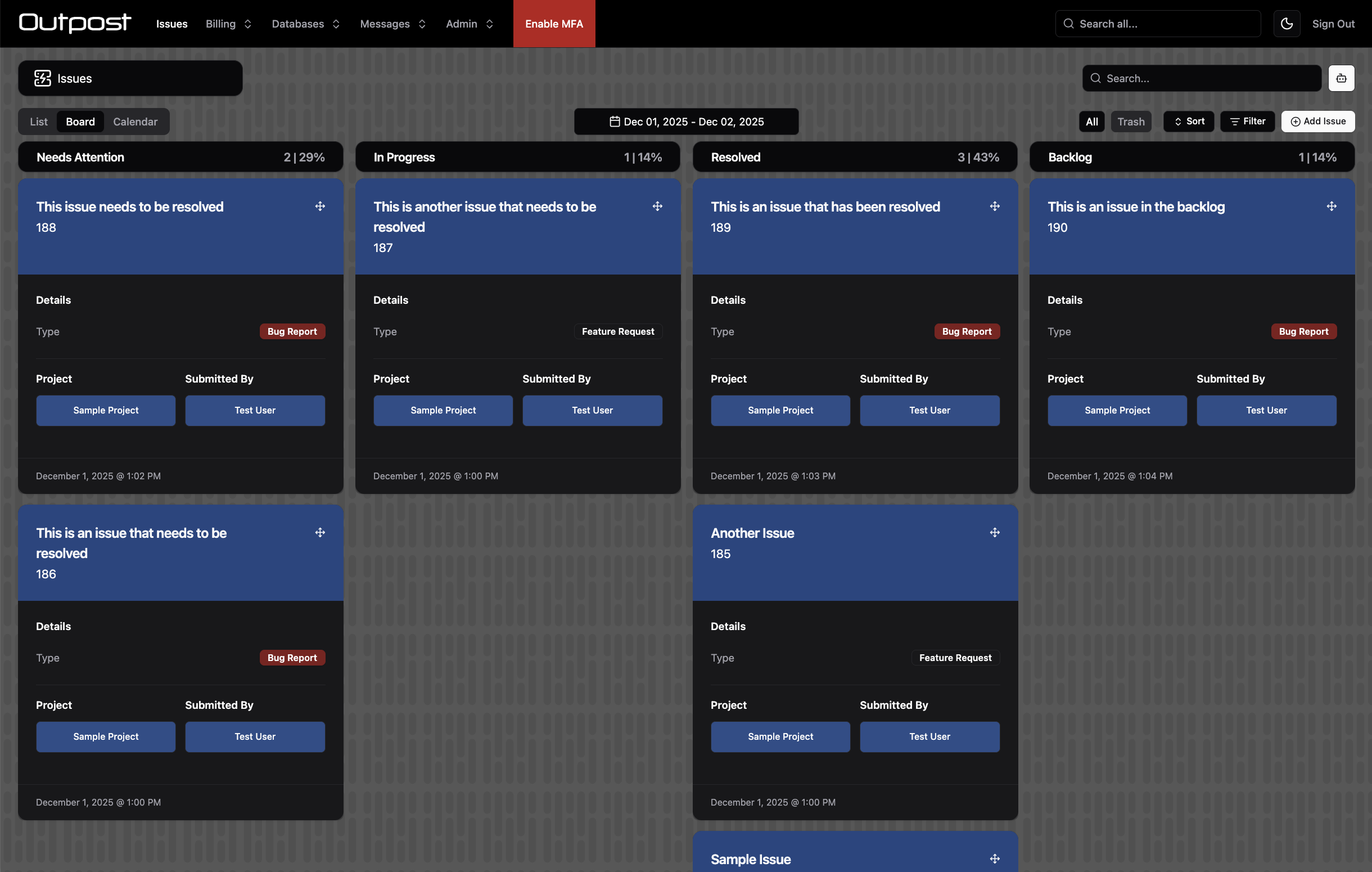
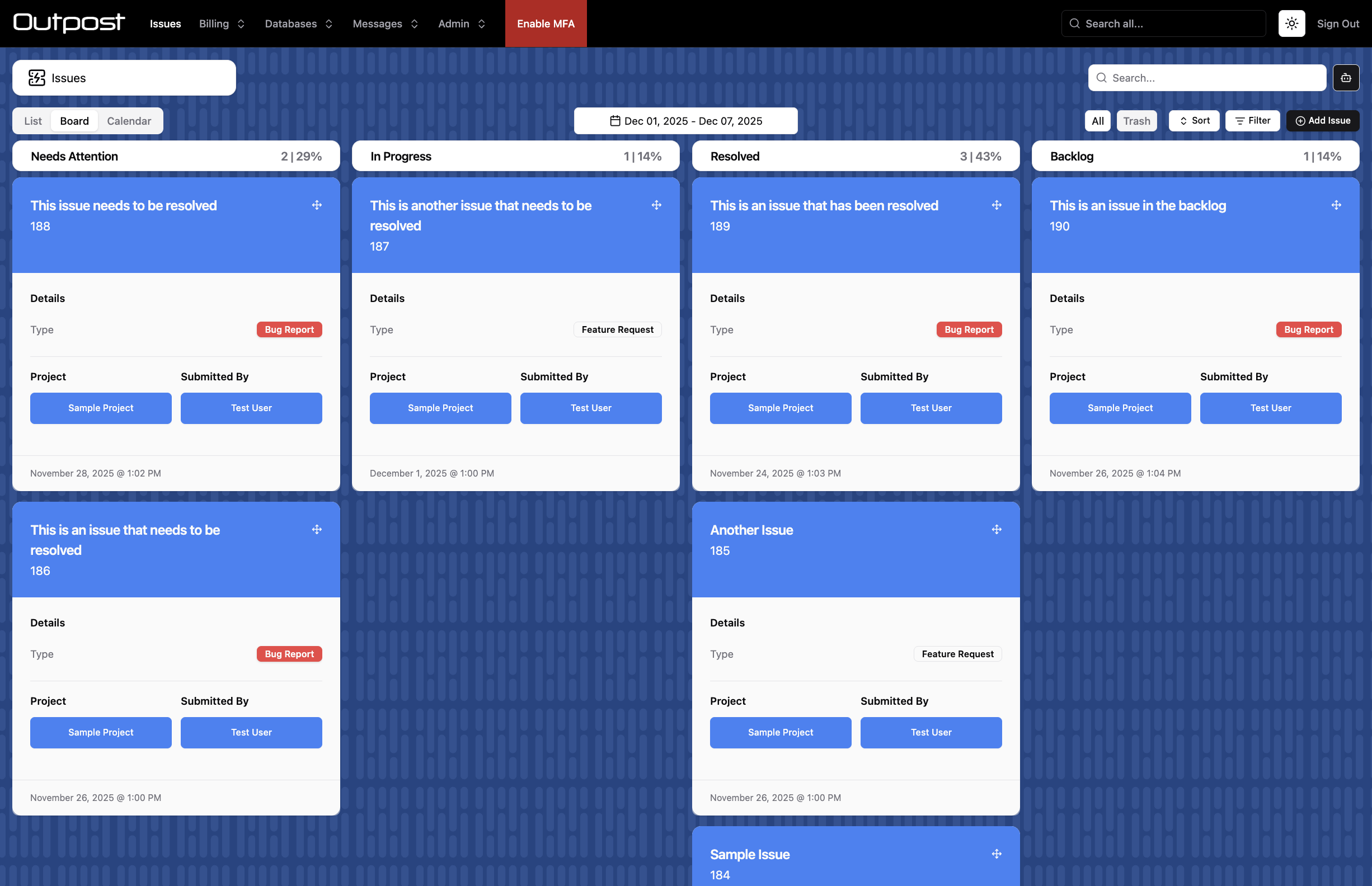
type CardsConfig = {
title?: string
roles?: string[]
statusField?: string
excludeValues?: string[] | number[]
headerField: string
maxHeaderLines?: 1 | 2
sections: {
title?: string
fields: string[]
blocks?: boolean
large?: boolean
maxSectionLines?: 1 | 2 | 3 | 4
collapse?: "sm" | "md" | "lg" | "xl" | "2xl" | ((record?: StokerRecord) => "sm" | "md" | "lg" | "xl" | "2xl")
}[]
footerField?: string
maxFooterLines?: 1 | 2
cardClass?: string
}
CardsConfig | (() => CardsConfig | Promise<CardsConfig>)
title: Customise the title for the board tab. Defaults to "Board".
roles: The user roles that can view the board
statusField: The field that will define the columns for the board. Must be a String or Number field with values set, or a Boolean field. Not required if admin.statusField has already been set.
excludeValues: Exclude status field values from the board
headerField: The header to be shown on cards on the board
maxHeaderLines: The number of lines for the header field text
sections: Return an array of sections that will display on cards.
section.title: The title for the section
section.fields: The fields to display in the section
section.blocks: Show multiple columns of fields, rather than listing fields down the card vertically.
section.large: Show a large field value
section.maxSectionLines: the number of lines for field text.
footerField: The header to be shown on cards on the board
maxFooterLines: The number of lines for the footer field text
collapse: Only relevant when blocks is set to true. Hide the outermost block at this screen size. Helps with responsiveness.
cardClass: Tailwind classes to apply to the card component
images
type ImagesConfig = {
title?: string
roles?: string[]
imageField: string
size: "sm" | "md" | "lg"
maxHeaderLines?: 1 | 2
}
ImagesConfig | (() => ImagesConfig | Promise<ImagesConfig>)
Show a list of image cards with infinite scroll.
title: Customise the title for the images tab. Defaults to "Pics".
roles: The user roles that can view the images page
imageField: The field that contains the image URL for the record. Must be a String field.
size: The size for images.
maxHeaderLines: The number of lines for the header field text
map
Show a map view.
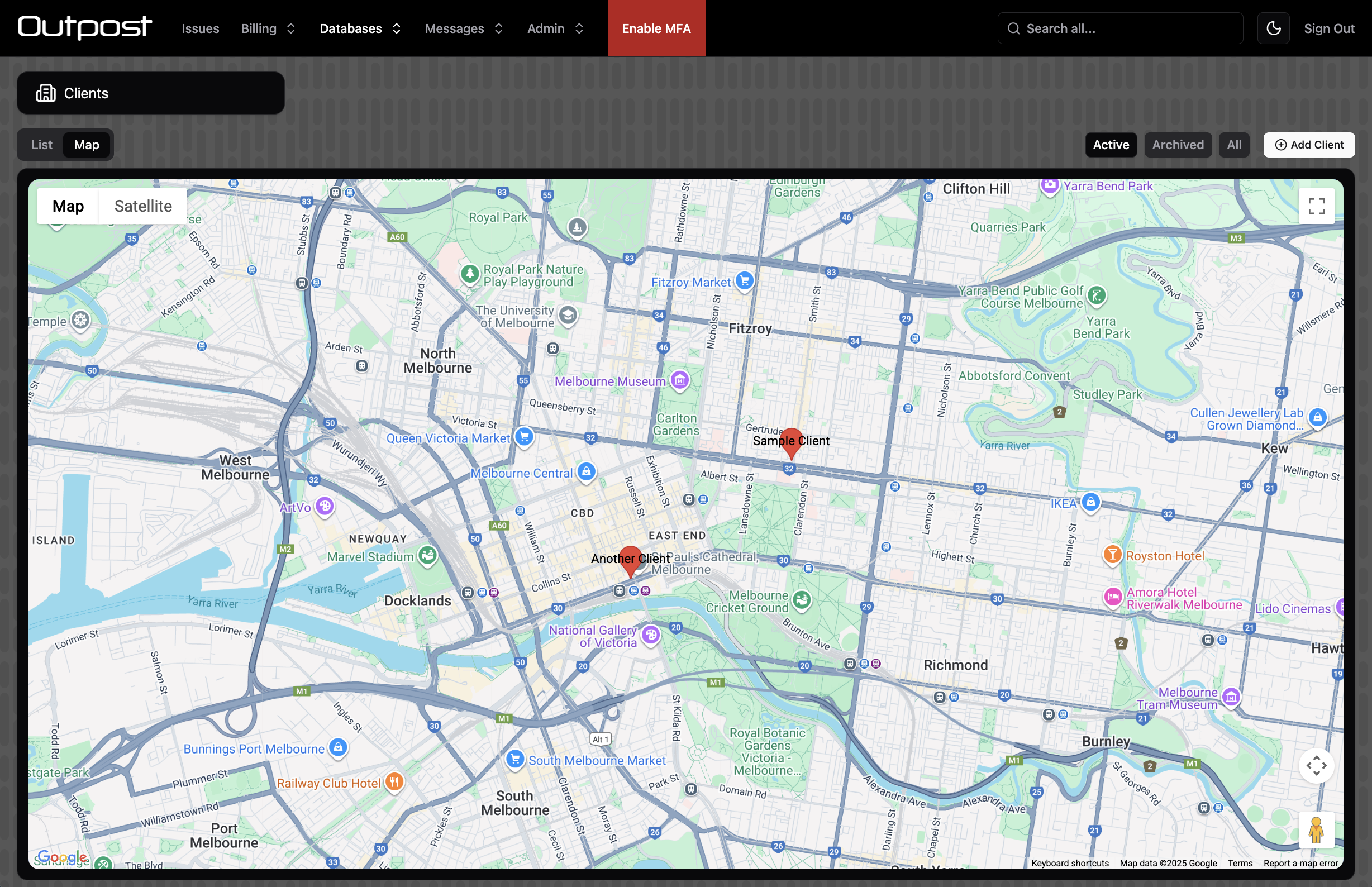
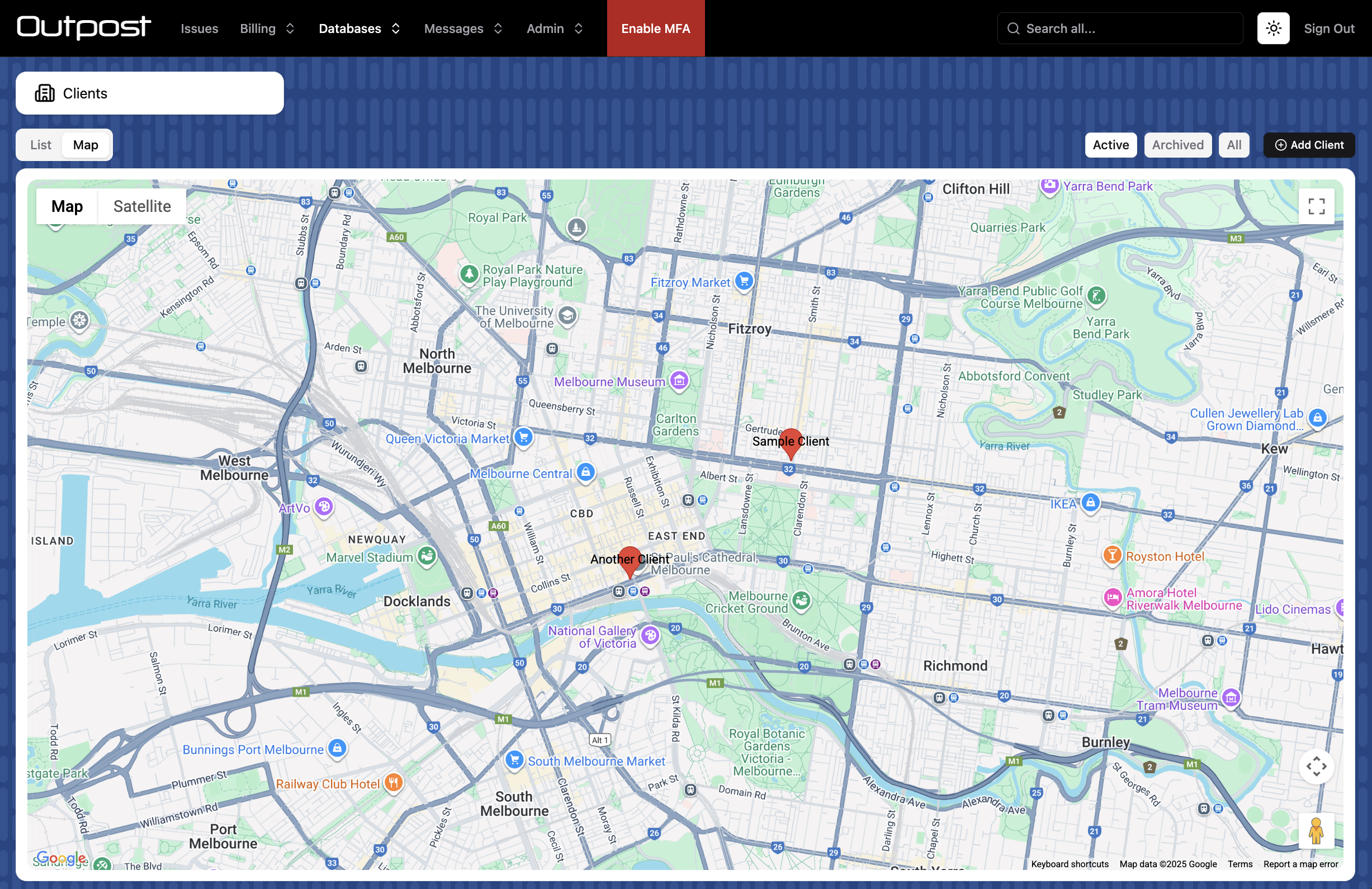
type MapConfig = {
title?: string
roles?: string[]
coordinatesField?: string
addressField?: string
center: {
lat: number
lng: number
}
zoom: number
noLocation?: {
title: string
}
}
MapConfig | (() => MapConfig | Promise<MapConfig>)
title: Customise the title for the map tab. Defaults to "Map".
roles: The user roles that can view the map page
coordinatesField: The field that contains coordinate values for the record. Must be an Array field.
addressField: Alternatively to the above, provide a String field with an address.
center: The starting coordinates for the map
zoom: The starting zoom value for the map.
noLocation: Provide a title (i.e. "No Address") to show a column of records without coordinates / an address. Records can be dragged onto the map (coordinatesField only).
calendar
type CalendarConfig = {
title?: string
roles?: string[]
startField: string
endField?: string
allDayField?: string
color?: string | ((record: StokerRecord) => string)
fullCalendarLarge?: CalendarOptions
fullCalendarSmall?: CalendarOptions
resourceField?: string
resourceTitleField?: string
unscheduled?: {
title: string
roles?: string[]
}
dataStart?: { days: number } | { weeks: number } | { months: number } | { years: number }
dataEnd?: { days: number } | { weeks: number } | { months: number } | { years: number }
dataStartOffset?: { days: number } | { weeks: number } | { months: number } | { years: number }
dataEndOffset?: { days: number } | { weeks: number } | { months: number } | { years: number }
}
CalendarConfig | (() => CalendarConfig | Promise<CalendarConfig>)
Show a calendar view.
title: Customise the title for the calendar tab. Defaults to "Calendar".
roles: The user roles that can view the calendar page
startField: A Timestamp field that specifies the start date for records on the calendar.
endField: A Timestamp field that specifies the end date for records on the calendar. If omitted, the start date will be used.
allDayField: A Boolean field indicating whether records are all-day.
color: The color for the provided record's event on the calendar
fullCalendarLarge: Fullcalendar options for the calendar at desktop screen sizes
fullCalendarSmall: Fullcalendar options for the calendar at mobile screen sizes
resourceField: A relational field that specifies a parent resource. Used for Fullcalendar features that require "resources".
resourceTitleField: A field in the resourceField collection that will act as a title
unscheduled: Show a column of unscheduled records. Only relevant if preloadCache.range is present for the user role. Records can be dragged onto the calendar.
dataStart: How far into the past to load records for
dataEnd: How far into the future to load records for
dataStartOffset: The threshold at which more past records will be loaded
dataEndOffset: The threshold at which more future records will be loaded
When both the preload cache range and the calendar are enabled, the system will calculate the maximum possible date range from the start and end dates for each. It will then load data for the calculated date range. You may want to keep the initial date ranges for each small, in order to reduce the amount of data initially loaded.
These limitations apply if you are NOT using the preload cache:
- Records will appear on the calendar based on their start date only.
- The calendar start date field must be a required field.
- If you use a range filter, its field must match the calendar start date field.
The calendar requires a Fullcalendar license
filters
type SelectFilter = {
type: "select"
field: string
title?: string | (() => string)
roles?: string[]
condition?: (value: boolean | string | number | undefined) => boolean
style?: "select" | "radio" | "buttons"
}
type RelationFilter = {
type: "relation"
field: string
title?: string | (() => string)
roles?: string[]
constraints?: [string, "==" | "in", unknown][]
}
type RangeFilter = {
type: "range"
field: string
selector?:
| "range"
| "week"
| "month"
| ("range" | "week" | "month")[]
| (() => "range" | "week" | "month" | ("range" | "week" | "month")[])
startOffsetDays?: number
startOffsetHours?: number
endOffsetDays?: number
endOffsetHours?: number
}
Filter[]
Return an array of filter objects (specified above). Filters will appear in the right-hand-side filter drawer on the list page.
"Select filters" allow you to filter the list by a field with values set.
"Relation filters" allow you to filter by a related field. The "constraints" option lets you filter the list of related values using a Firestore where() query.
"Range filters" allow you to filter by a Timestamp field. See preloadCache.range for more information on what the options do.
metrics
type Metric = {
type: "sum" | "average" | "count"
field?: string
title?: string
roles?: string[]
decimal?: number
prefix?: string
suffix?: string
textSize?: "text-xl" | "text-2xl" | "text-3xl"
}
type Chart = {
type: "area"
dateField: string
metricField1?: string
metricField2?: string
title?: string
roles?: string[]
defaultRange: "90d" | "30d" | "7d"
}
(Metric | Chart)[] | (() => (Metric | Chart)[] | Promise<(Metric | Chart)[]>)
Show metrics (numerical counters) and a chart at the top of the list page.
We recommend 1-2 metrics and a chart.
Collection Hooks
When importing modules that are web-only or server-only, be sure to:
- Install them using
external.packages.json - Guard their use by wrapping code in:
if(sdk === "web") {
...your web code goes here...
}
if(sdk === "node") {
...your server code goes here...
} - Import them dynamically i.e.
await import("firebase/firestore")
This lets you write web and server code in the same file.
You can also write your own modules in the src/web and src/node folders and import modules statically there. In this case, you can only use one import per line i.e. import { getFirestore } from "firebase/firestore"
Server code protection: During the build process, server-only code blocks are automatically stripped from the client bundle:
if(sdk === "node")blocks are removedelseandelse ifblocks followingif (sdk === "web")guards are removed- Code in
src/nodeis stripped to export names only
Important: Code outside of these guard blocks WILL be sent to the client and will run on the client.
For highly sensitive server operations, consider using custom cloud functions instead.
Auto-incremented numbers will be "Pending" in hooks.
In the Web SDK, postWrite, postError and postOperation hooks will not fire if the window is closed before the operation completes. Consider using a cloud trigger function instead.
- Hooks will not run on retries for offline writes and unique field auto-correction.
preOperation
(
operation: "read" | "create" | "update" | "delete",
data?: StokerRecord,
docId?: string,
context?: any,
batch?: WriteBatch,
originalRecord?: StokerRecord
) => boolean | void | Promise<boolean | void>
Fires before a read or write operation.
Return false to cancel the operation.
preRead
(
context: any,
refs: unknown[],
multiple?: boolean,
listener?: boolean,
) => void | Promise<void>
Fires before a read operation.
preValidate
(
operation: "create" | "update",
record: StokerRecord,
context: any,
batch?: WriteBatch,
originalRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => { valid: boolean; message?: string } | Promise<{ valid: boolean; message?: string }>
Fires at write validation time. This is where you can define custom validation logic.
Return an object with a boolean indicating whether validation passed, and a message to display to the user if validation has failed.
preWrite
(
operation: "create" | "update" | "delete",
data: StokerRecord,
docId: string,
context: any,
batch?: WriteBatch,
originalRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => boolean | void | Promise<boolean | void>
Fires before a write operation.
Return false to cancel the operation.
preDuplicate
(data: Partial<StokerRecord>) => boolean | void | Promise<boolean | void>
Fires before a duplicate operation in the Admin UI.
Return false to cancel the operation.
postOperation
(
operation: "read" | "create" | "update" | "delete",
data?: StokerRecord,
docId?: string,
context?: any,
retry?: boolean,
originalRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => void | Promise<void>
Fires after a read or write operation.
postRead
(
context: any,
refs: unknown[],
doc: StokerRecord | undefined,
listener?: boolean,
) => void | Promise<void>
Fires after a read operation.
postWrite
(
operation: "create" | "update" | "delete",
data: StokerRecord,
docId: string,
context: any,
retry?: boolean,
originalRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => void | Promise<void>
Fires after a write operation.
postWriteError
(
operation: "create" | "update" | "delete",
data: StokerRecord,
docId: string,
context: any,
error: unknown,
retry?: boolean,
retries?: number,
originalRecord?: StokerRecord,
) => void | Promise<void>
Fires when a write operation encounters an error.
This hook may file multiple times per write, so be sure to write idempotent code.
preFileAdd
(
record: StokerRecord,
fullPath: string,
filename: string,
permissions: FilePermissions,
) => boolean | void | Promise<boolean | void>
Fires before a file is uploaded.
Return false to cancel the operation.
preFileUpdate
(
record: StokerRecord,
update:
{ type: "rename"; oldPath: string; newPath: string } |
{
type: "permissions"
path: string
originalPermissions: FilePermissions
permissions: FilePermissions
},
) => boolean | void | Promise<boolean | void>
Fires before a file is updated.
Return false to cancel the operation.
postFileAdd
(
record: StokerRecord,
fullPath: string,
filename: string,
permissions: FilePermissions,
) => void | Promise<void>
Fires after a file is uploaded.
postFileUpdate
(
record: StokerRecord,
update:
{ type: "rename"; oldPath: string; newPath: string } |
{
type: "permissions"
path: string
originalPermissions: FilePermissions
permissions: FilePermissions
},
) => void | Promise<void>
Fires after a file is updated.
setEmbedding
(record: StokerRecord) => string | Promise<string>
Calculate an embedding value for the record.
Only assign AI chat access to roles that have access to ALL fields used to calculate embeddings!